GOLD ISN'T AN INVESTMENT
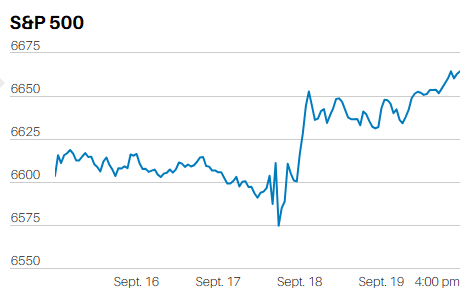
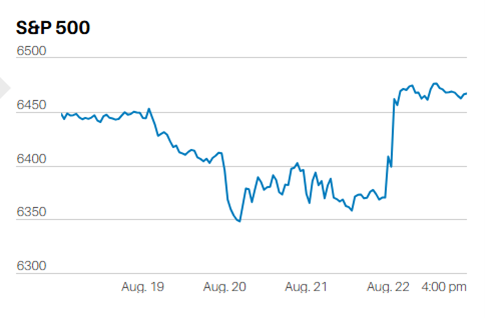
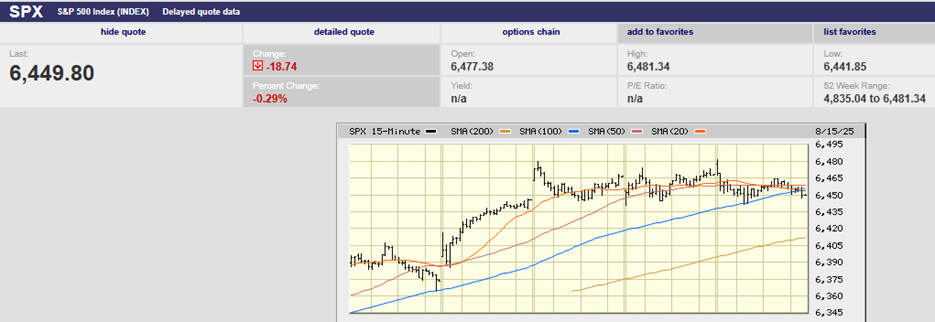
The S&P 500 fell 1.2% last week. It closed at 3337.75. Two weeks ago, we wrote, “In technical terms the market put in a three-day top on Friday. The oversold bounce may be over. Odds now favor a pullback over the next week or two. A weak market should sell-off this week; how far and how fast lets us know whether investors are still scared and motivated to take profits or not. Rising volatility over the next week or two is also a real possibility.”
We didn’t get the sell-off we expected two weeks ago; a pullback may have started on Thursday though. Again, whether we get follow through this week will tell us much about the current mood of investors. The S&P 500 closed near its Friday low after giving up 1.6% in the preceding day-and-a-half of trading. Traders were apparently happy to close out positions before the weekend, an indication they aren’t very confident the selling is over. The index is back to its 20-day moving average. The January swoon took it down to its 50-day moving average. The S&P 500 would need to fall to 3275 to test the 50-day, a decline of not quite 2%. The 200-day sits at 3040, almost 9% lower than the current level and a bit more than 10% off the most recent record high.
A 10% pullback is a run-of-the-mill correction, but I bet it will feel much more painful to spoiled investors if it happens in the coming weeks.
Economic Data
The yield curve is inverted out to ten years once again. The three-month/five-year is inverted as well. The media isn’t trumpeting the inversion, perhaps because the popular measure is the two-ten curve. However, it’s the three-month/five-year that has the perfect track record of calling recessions with no false signals. Furthermore, the Federal Reserve uses the three-month/ten-year as a predictor of the probability of recession within the next twelve-months and it’s inverted as well. Banks can’t lend profitably when short rates are higher than long rates. Less lending means less credit creation and less credit creation means slower economic growth, particularly given that the current expansion is heavily dependent on debt. The 30-year Treasury fell to its lowest level in American history last week according to Barron’s. The bond market certainly isn’t predicting strong economic growth in 2020.
The IHS Markit composite purchasing managers’ index fell sharply in February into contractionary territory, according to Barron’s, led by a plunge in new orders to the lowest level since the dark days of 2009. The PMI is widely seen as an accurate and timely indicator of business conditions. Perhaps the bond market is on to something.
Gold as insurance
Gold is misunderstood by most investors, or rather its place in a properly diversified portfolio is misunderstood. Gold is insurance. Gold is also a wonderful diversification tool. The Federal Reserve is responsible for maintaining price stability. The FOMC is changing the definition of price stability right before our eyes. It defines price stability as 2% inflation. Two percent inflation means an almost 40% pay cut to retirees over a 20-year retirement. There is nothing stable about 2% inflation.
Or rather the Federal Reserve used to define price stability as 2% inflation. More recently it’s decided that if inflation averages 2% over a business cycle it’s done its job. Not 2% out-of-pocket inflation as measured by the Consumer Price Index (CPI), but 2% personal consumption expenditure (PCE) inflation which incorporates made up pricing (think owner equivalent rent). Gold is the insurance you take out in case the Federal Reserve accidently sparks mid-to-high single digit out-of-pocket inflation (or worse) as it pursues its easy money policies.
Gold also provides diversification for those who care about risk-adjusted returns. Gold has a low correlation with both stocks and bonds. Higher risk-adjusted returns are the name of the game. A portfolio that earns 10% with twice the volatility is inferior to a portfolio that earns 8%. Comfortable with the higher volatility? Use leverage to double up volatility while earning 16% instead of the inferior 10% return. Gold makes a stock, bond, and real estate portfolio more efficient.
What gold isn’t is an investment. It provides no cash flow and creates no wealth. People that own large amounts of gold with the expectation that the price will go up are speculating. Gold has a place in a properly diversified portfolio in limited amounts. Just don’t be fooled into thinking you’re investing in gold.
Regards,
Christopher R Norwood, CFA
Chief Market Strategist