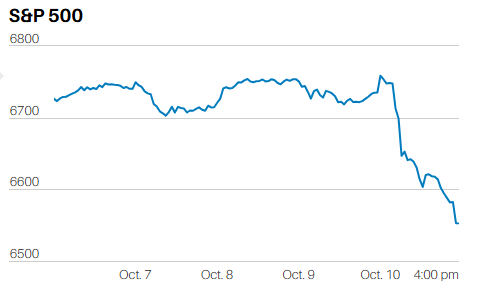
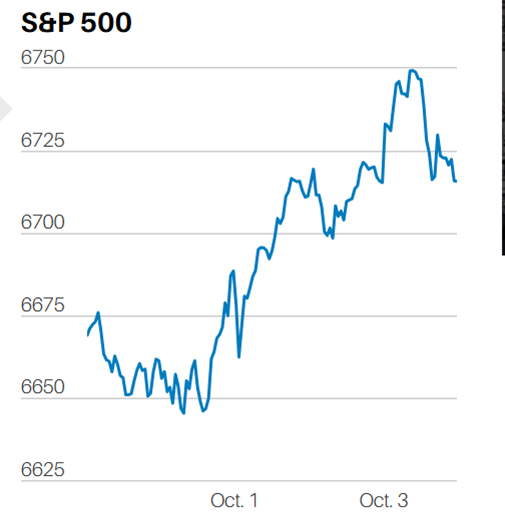
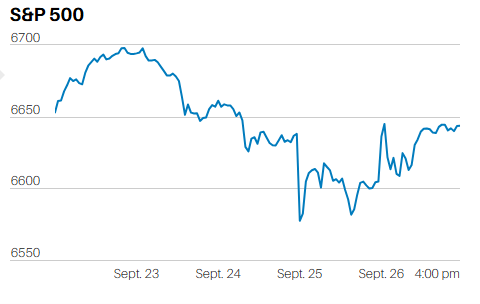
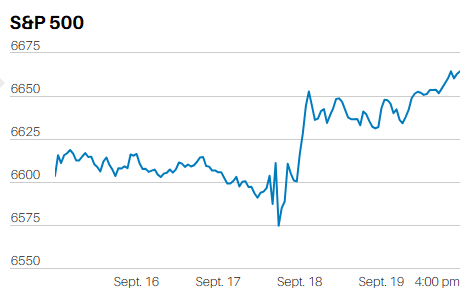
Sometimes it is easy to measure performance. The winner of a 100 meter dash is whomever crosses the finish line first. The winning time is directly measurable, using a stop watch – these days down to the hundredths of a second. Run the race faster than it has ever been run before and you are a world record holder…..or are you?
Turns out that you may or may not be the new world record holder, depending on whether your time was wind-aided or not. A sufficient tail wind will negate your world record, perhaps unjustly if the wind measuring equipment is mis-calibrated.
Measuring things, in fact, ranges from fairly straightforward to down right difficult. There is even a field of study, measurement theory, that occupies the time of some very smart people. Or as the Encyclopedia Britannica relays: “Measurement, the process of associating numbers with physical quantities and phenomena. Measurement is fundamental to the sciences; to engineering, construction, and other technical fields; and to almost all everyday activities. For that reason the elements, conditions, limitations, and theoretical foundations of measurement have been much studied.”
So in actuality, measuring the speed of a race, the efficacy of a drug, or the return of a mutual fund can be far from straightforward. One well understood phenomena associated with measurement theory (at least well understood by the measurement theory folks) is that all too often the way in which you measure something determines the results obtained from your experimental model.
Measuring investment performance, in point of fact, is devilishly difficult. Appropriate benchmarks, risk-adjusted returns, relative performance, absolute performance, statistically meaningful time periods, throw it all into the performance pot, stir vigorously and end up with… controversy.
Is a return of 8% in a small cap stock portfolio better or worse than a return of 8% in a large cap stock portfolio? Is an absolute return of 10% a better result than an absolute return of 7%? Does a balanced mutual fund (stock/bond) outperforming the S&P 500 on a trailing one year basis mean the mutual fund manager added value through active management? Is performance relative to an appropriate benchmark a meaningful indicator of portfolio manager skill over a one-year period?
The answers are: worse ; maybe but not necessarily; again maybe but not necessarily; and no.
By way of explanation:
Small cap stocks are more volatile than large cap stocks. Volatility is the most common measure of investment risk – though certainly not the only one. Small cap stocks also have a higher rate of return historically than large cap stocks. For instance, the Russell 2000 has returned around 125% since 2000 while the S&P 500 is up only about 30% (both returns are net of dividends). Now we can’t actually say the small cap portfolio earning 8% in a given year was a worse performance because short-term results aren’t particularly meaningful. But we can say the small cap result was worse because small cap stocks are more risky, as measured by volatility, than large caps. Therefore, on a risk-adjusted basis, we should expect a higher rate of return from our small cap portfolio. More risk requires higher rates of return to justify exposure to that additional risk.
Likewise, the 7% return might actually be a better result than the 10% return if the amount of risk assumed was sufficiently low. Earn 7% in a portfolio with a standard deviation of 5% and you are far better off than if you are earning 10% in a portfolio that has a standard deviation of 50%. Why? With the 7% portfolio you will earn between 2% and 12% two-thirds of the time while the higher earning 10% portfolio will return anywhere from minus 40% to plus 60% two-thirds of the time. You simply aren’t getting enough additional return to take on that kind of volatility. And, there is a distinct possibility that the 7% portfolio will actually outperform the wildly volatile 10% portfolio over time because of how returns compound. (e.g. 5%, 12%, 2%, 6%, 3% will beat minus 40%, 50%, minus 20%, 15%, 10% by a wide margin… do the math!)
What about the balanced fund manager beating the S&P 500? Well American Funds is out touting the fact that some of their stock/bond funds have outperformed the S&P 500 over the last 15 years. Leaving aside the fact that American Funds wasn’t kind enough to tell investors which of its many funds would outperform the S&P 500 before the fact, the main problem is with the apples to oranges comparison. The S&P 500 is an index of large U.S. stocks. Bonds have had a pretty good 15-year run and are almost certainly responsible for increasing at least some of American Fund’s absolute returns above the S&P 500, which has only returned around 4% annually since the tech bubble popped. So basically American Funds is saying that the color orange is better than popcorn.
Yes, measuring performance turns out to be not very straightforward at all, whether it’s attempting to verify a new world record, measuring gross domestic product or determining if investment performance is good or….bad.