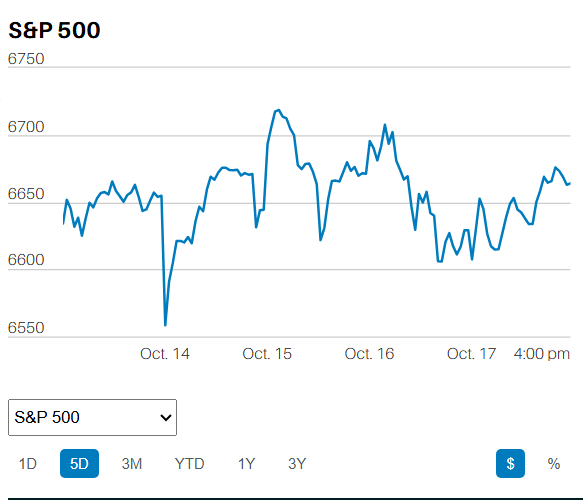
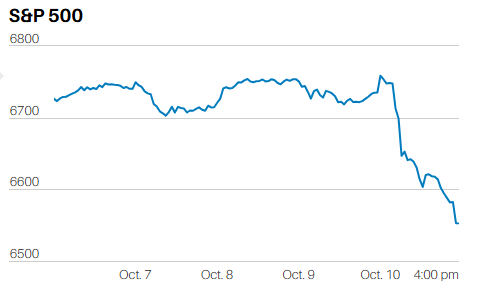
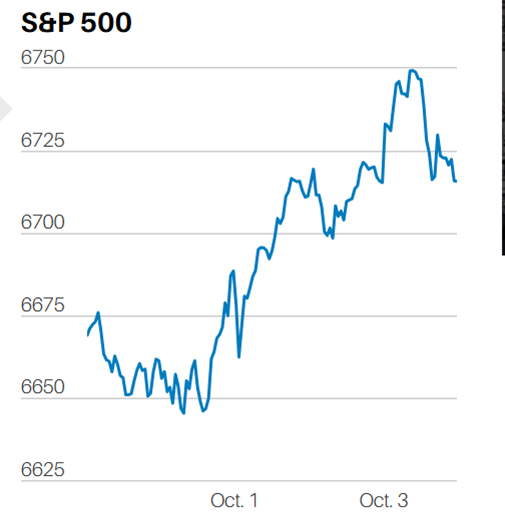
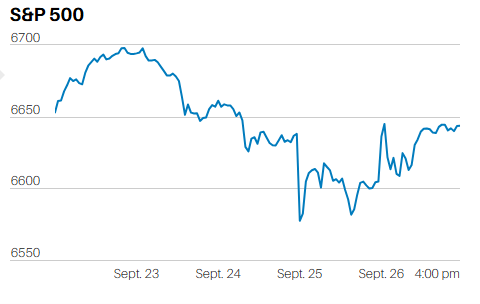
The temptation for investors will be to sell their losers and buy the winners; or perhaps, this year, buy the losers that lost the least. Exactly the opposite of what they should do.
We just aren’t wired to make good financial decisions. We’re just not. We are chock full of biases that seemingly make it impossible to even earn what the markets are giving us . . . if only we’d take it. The most famous study on that score was done by Dalbar, who did its original report back in 1994, and has updated it yearly since. The research firm found that the average investor is awful, simply awful, at investing. For instance, the 2004 study showed that “the average investor earned 3.51% and those who pursued a consistent investment strategy earned 6.8% over the prior 20 years. Over the same period, the S&P grew by 12.98%.” (Business Wire, 1 April 2004). Let that sink in for a moment. The average investor underperformed the S&P 500 by more than 9% over a 20-year period, resulting in a tremendous amount of foregone wealth for individuals.
And investors haven’t gotten any better in the succeeding 13 years. The 2017 Dalbar report stated that, “The 20-year annualized S&P 500 return was 7.68%, and the average equity fund investor’s return was only 4.79%, a gap of 2.89%. The average fixed-income mutual fund investor underperformed the Bloomberg Barclays Aggregate Bond Index by a margin of 1.42%. The broader bond market realized a return of 2.65%, while the average fixed-income fund investor’s return was 1.23%.” (Market Watch, Oct 2017).
Underperformance of 2.89% in stocks over a 20-year period means tens of thousands in lost profits for individuals. How is it we’re so terrible at investing?
Turns out humans are hard wired to fail when it comes to investing. We have myriad biases that work against us. Overconfidence bias leads us to believe that we’re all Warren Buffet. Heuristics are rules of thumb that lead us to believe good companies are good investments and bad companies are bad investments – without taking the price into account. And then there is recency bias:
Recency bias is our tendency to overweight near-term, past results and underweight longer-term results, and it causes us to double down on recent outperformers and shun recent losers, pretty much exactly the opposite of what we should typically do given the markets propensity to revert to the mean. Translation? Investors often review their mutual fund performance at year end, sell their losers and buy more of what’s working. Without realizing it, investors are concentrating their portfolios rather than maintaining an appropriately diversified portfolio. It’s all about correlation. A properly diversified portfolio will always, by definition, hold assets that are underperforming, while other assets are outperforming. In fact, the lack of correlation is what makes the portfolio diversified. Selling the losers and buying more of what’s working means buying assets that are correlated with your winners, which means less diversification.
The current year is going to prove very challenging for investors. They will be tempted to make wholesale changes to their portfolios to rid themselves of losing investments. And there are lots of losing investments they’ll want to dump. In fact, most asset classes are showing losses in 2018. Target date funds, which are broadly diversified portfolios, are down through 10 December, all of them, according to Morningstar. Since target date funds are diversified portfolios, they make a good benchmark with which to measure a diversified strategy. The average target date fund is down 4% through 10 December and not a single one of the 664 target date funds, holding $1.1 trillion in assets, have a positive return for the year - not a single one.
Yes, the temptation for investors will be to sell their losers and buy the winners; or perhaps, this year, buy the losers that lost the least. Exactly the opposite of what they should do, which is to rebalance their portfolio back to the original allocation by selling some of those assets that outperformed and buying those that underperformed. But most investors likely won’t because, hey, who wants to buy a loser?