Rising unemployment and slowing wage growth is the goal.
Recession is the Risk.

Market Update
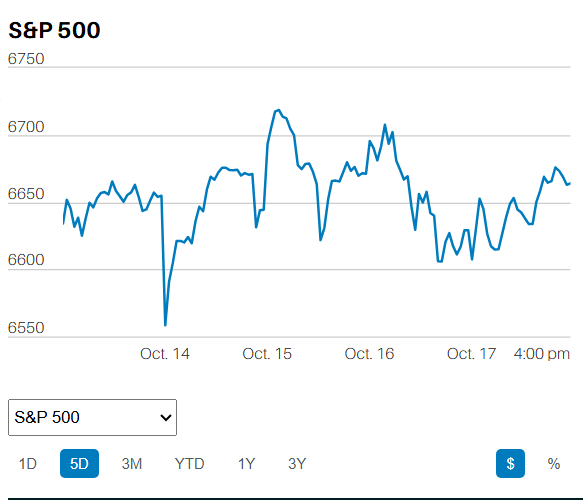
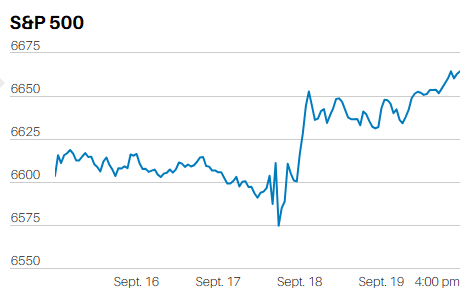
The S&P 500 climbed 2.4% to finish the week at 4,505.42. The Nasdaq rose 3.3%. The two-year Treasury yield fell to 4.7% from above 5% the prior week. We wrote last week that, "Buyers couldn’t push the S&P above 4,440 (on Friday), although they tried for almost 45 minutes. Having failed to advance past 4,440, the S&P started falling around 1:30 p.m. and closed near its low for the day. Closing near its low on Friday means the selling is more likely to continue Monday.” The selling did continue Monday morning. The S&P traded down another 9 points before bottoming at 4,389.92 around noon. Monday’s low was the low for the week though.
The S&P advanced to 4,443.64 in the last fifteen minutes of trading on Tuesday. It closed at 4,439.26, below the 4,440 resistance. A target was set though with the temporary advance above 4,440. Remember, the S&P had tried for 45 minutes to advance past 4440 the prior Friday without success. The market ran into selling at that same 4,440 level on Tuesday. The algorithms took care of the resistance level at the open on Wednesday by gapping up to 4,470. The excuse was the better-than-expected inflation report released before the market opened. It was only an excuse though as traders battled in their zero-sum game of tug-of-war.
The Fed has made it clear that it will raise rates at the July 25-26 meeting. It has made it clear that it needs to see wage growth slow to 3.0% to 3.5% before it will declare victory in its inflation fight. It has made it clear that the CPI report would have no impact on its July decision. It has also made it clear that it may hike again depending on the next couple months of data.
Former Fed Vice chair Richard Clarida was on Bloomberg before the CPI report was released. He said unequivocally that the CPI report would have no impact on the Fed’s decision to raise in July. He was speaking for the Fed although no longer with the Fed. It is a common practice for the Fed to use former officials to get the word out. The market's gap up open was about the algorithms needing to vanquish 4,440 before profit taking set in. It was not about equity investors deciding to buy based on improving fundamentals.
But the drop in the two-year yield that began on July 6th does signal that bond investors expect a lower fed funds rate in 2024. (The two-year tracks the fed funds rate.) The two-year yield began falling the week before last, well in advance of the CPI report. A declining two-year yield lines up with the fed funds futures market.
The CME FedWatch tool is assigning a 93% chance of a rate hike in late July. A hike would take the fed funds rate to 5.25%-5.50%. There is a 70% chance that the funds rate will be at 5.25% or higher at year end. Investors are pricing in rate cuts after year-end, which lines up with a falling two-year yield. There is only a 25.7% chance of the fed funds rate being at 4% or higher by the end of 2024 according to the CME FedWatch tool. There is a 50.4% chance that the funds rate will be between 3.5% and 4% by year end 2024. That implies at least five 0.25% cuts by the end of 2024, assuming one more quarter point hike in July. Wall Street is betting on a quick reversal of Fed policy over the next 17 months. Such a sharp reversal will only occur in a recession.
Falling inflation is touted as the reason for the 2023 stock market rally. Yet the rally is about a handful of stocks. Seven stocks with a combined $11 trillion in market value contributed 73% of the first half gains, according to Barron’s. Apple, Microsoft, Amazon, Alphabet and Nvidia have a 47% weighting in the Nasdaq. Those five stocks make up 24.2% of the S&P 500. The Russell 1000 Value index is up 2.9% in 2023. The Russell 2000 (small cap) Value index is flat on the year. Falling inflation hasn't helped most stocks. Likewise, the big five are flying on AI hype not disinflation.
Most stocks haven’t gone anywhere for good reason. Earnings have been falling. S&P earnings declined 1.8% in Q4 2022. They fell 2.8% in Q1, are expected to fall 8.9% in Q2 and 0.5% in Q3. That is four quarters in a row of declining earnings. Small wonder that most stocks aren’t participating in the gains in 2023. There is good reason to expect continued pressure on earnings. Falling inflation means slower nominal GDP growth which means slower nominal revenue growth. Slower revenue growth means pressure on profit margins, all else equal. Pressure on profit margins means cost cutting which means layoffs. Falling inflation leads to falling real GDP growth as well then. The consumer is 70% of the economy. Consumers can’t consume for long without income.
But if falling inflation IS the reason for the rally then investors should brace themselves. There is a good chance that inflation will start rising again in the next few months. The CPI rose 1.2% in June of 2022. The June 2023 CPI gain was 0.2% which means inflation fell by 1% year-over-year. The CPI was unchanged in July 2022. The year-over-year number is set to rise in July 2023 if the monthly number is greater than zero. In fact, the annual change in the CPI will be 3.9% in December if monthly inflation reverts to its quantitative-easing-era average in the second half of 2023, according to Bianco Research. The stock and bond markets aren't prepared for rising inflation into year end.
“Any additional disinflationary momentum will have to come from slower month-over-month gains in core services prices,” Gregory Daco, chief economist at EY Parthenon, wrote recently. He believes that energy prices, food prices, and core goods prices have stopped falling, according to Barron’s. Core CPI is currently 4.8%. That is well above the Fed’s target of 2%. Average hourly earnings are growing at a 4.4% clip, too fast for inflation to fall to 2%.
The Fed’s favorite measure of inflation hasn’t moved much in over a year. The 12-month trimmed mean PCE inflation rate was 4.6% in May down a tick from 4.7% in December 2022. The six-month trimmed mean PCE inflation rate is 4.3% down marginally from 4.4%. The PCE index is unlikely to move much lower without a decline in wage growth. Chairman Powell has stated wage growth of 3.0% to 3.5% is enough to push inflation down to 2%. That will require a rise in unemployment. All roads lead back to a recession. It’s a question of when it begins.
Economic Indicators
The NFIB survey rose to 91 in June from 89.4 in May but remained well below its average of 98. Small business owners remained concerned about inflation and labor quality. The number of owners expecting better business conditions over the next six months rose 10% from May. Most owners are still negative on future business conditions though. “Halfway through the year, small-business owners remain very pessimistic about future business conditions and their sales prospects,” said NFIB Chief Economist Bill Dunkelberg.
The consumer price index rose 0.2% in June, better than the 0.3% forecast. The core CPI year-over-year rose 4.8% down from 5.3%. Core PPI rose 0.1% in June up from 0.0% the prior month. The core PPI year-over-year rose 2.6% down from 2.8%. The PPI is a leading indicator of the CPI.
The Risk Premium Revisited
We wrote last week about the equity risk premium. An investor should expect a higher return from a riskier investment. The risk premium for stocks versus bonds has averaged between 3.0% and 3.5% over the last 20 years or so. It has averaged closer to 4.5% going back to the late 1800s. Currently, the risk premium is only around 1.1%.
One of Barron’s Roundtable guests referenced risk premium in this week’s edition. Rupal J. Bhansali is chief investment officer and portfolio manager of international and global equity strategies for Ariel Investments. She manages billions of dollars at Ariel.
Bhansali told Barron’s in this week’s edition that, “The U.S. 10-year Treasury yield is approaching 4%, and equity risk premiums should be at least 300 basis points above that to compensate for higher risk. This implies a 7% earnings yield on the S&P 500, or a price/earnings multiple of 14.28 times." She went on to point out that the S&P would need to trade down to 2856 for the equity risk premium to rise to 7%, assuming a recession and double-digit decline in earnings. The S&P would need to trade down to around 3,141 if current earnings forecasts are accurate. The S&P is currently above 4,500.
Small Caps Are Cheap
Ed Clissold, chief U.S. strategist at Ned Davis Research notes that the S&P 600’s earnings yield – the inverse of the index’s price/earnings ratio – is near a record low versus the S&P 500’s.
Monetary Tightening Without Rate Cuts
It is the real interest rate that counts. High real rates are restrictive. Negative real rates have been the norm for years now (free money). The real interest rate is the nominal rate minus inflation. The nominal rate is what you pay or receive. You need to subtract inflation from that amount to understand the true cost of money.
The Fed’s Summary of Economic Projections (SEP) shows a year end Fed funds rate of 5.6%. The Fed is forecasting a core PCE rate of 3.9% by year end. Based on the funds rate and PCE forecasts the real interest rate will be 1.7% by year end. The real interest rate will continue to increase as inflation falls. Monetary policy will tighten without rate cuts. The real rate will continue to rise even as the Fed starts cutting rates should the inflation rate fall faster than the funds rate. In other words, monetary easing might not happen as quickly as it did in the low-inflation era.

In past cycles the average Fed pause from the last rate hike to the first cut was eight months. In every case the stock market did not bottom until 13 to 33 months after the last hike. (see chart above). We can expect a continuation of tightening as the Fed hikes in July. We can expect further tightening after that because of falling inflation regardless of whether the Fed hikes a second time.
It will likely be next spring at the earliest before the Fed starts cutting. And then only if a recession has materialized. A stock market bottom isn’t likely to occur until at least August of 2024 if the July hike is the last. The questions are: What does the stock market do before it begins to price in a recession? And when does it begin to price in the recession?
Oh, and let's not forget about Quantitative Tightening. Equity investors are in a high-risk environment. Risk management is paramount.
Regards,
Christopher R Norwood, CFA
Chief Market Strategist