Rising Interest Rates Destroys Demand

Market Update
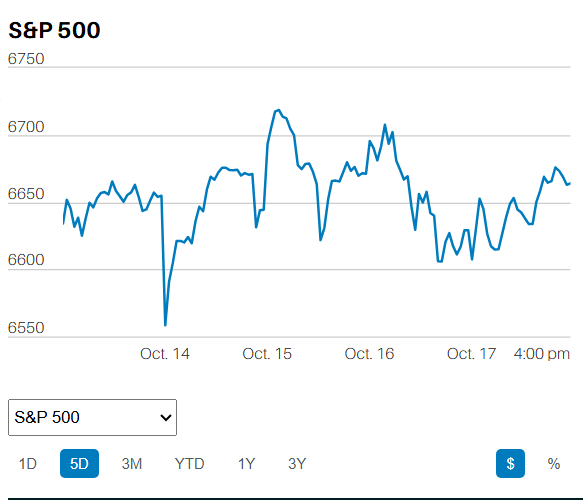
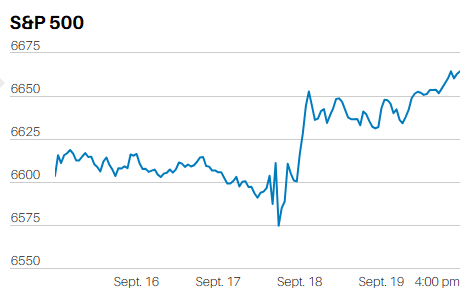
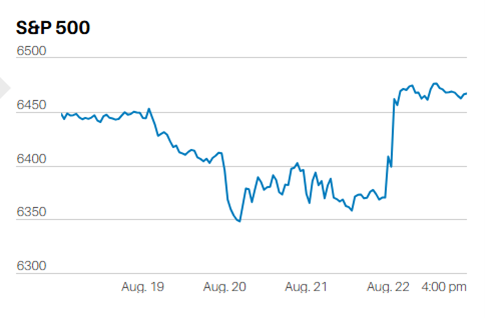
The S&P 500 lost 0.9% last week to close at 3863.16. The Nasdaq fell 1.6% and the Dow 0.2%. It would have been a bigger decline for all three stock indexes if not for Friday's strong gains. The S&P hit a high for the week of 3880.94 on Monday. It hit its low for the week Thursday morning in the first 45 minutes of trading. Investors bought Thursday's down opening and the S&P rose the rest of the day. The index gapped up at the open Friday morning but stalled at 3860. Traders attempted to best that level four times starting at 11 a.m. The S&P finally punched through 3860 in the last 15 minutes of trading Friday. The market is likely to continue to try to move higher early in the coming week.
We wrote last week that, “The S&P struggled with 3920 on Friday.” We wrote two weeks ago that, “We may see another attempt at the 3945.86 high following the 4th of July weekend. An advance past 3945.86 clears the way for a test of resistance at 4177. Until we clear 4177 the short-term trend is down.” Nothing has changed. The S&P needs to push through 3918.5 (the 8 July high) followed by the 50- moving average at 3940. Resistance at 3945.86 is next. Only then can the S&P take a run at 4177. Earnings season will need to surprise if the market is going to climb. Earnings season started last week but most companies haven't reported yet.
A disappointing earnings season will cause the market to continue to fall. There is support at 3721.56 hit 14 July. Additional support exists at 3738.67. A breach of the June 17th low of 3636.87 would confirm the downtrend is still in place. Meanwhile, the S&P is in a month-long trading range. Earnings season will put an end to the trading range one way or the other.
Earnings season is likely to disappoint. Specifically, guidance for the second half of the year will probably be negative. It isn’t obvious that the stock market will sell the news though. The first half was bad. The second quarter was awful. It is possible that the market is set up for a sell the rumor buy the news move higher. Call it 60/40 that the S&P 500 moves higher during earnings season. Of course, that means a 4 out of 10 chance it moves lower instead.
Economic Indicators
Inflation expectations are important to the Federal Reserve. Inflation can become entrenched when people are expecting it. Three-year inflation expectations fell to 3.6% from 3.9% the month before. The five-year peaked at 3.57% on 23 March and has fallen to 2.59% as of Friday. The 10-year inflation expectation peaked at 3.02% on 21 April and is now at 2.36%. Falling inflation expectations are a positive for the stock market since it means fewer Fed rate hikes.
The headline CPI number was worse than expected, however. Inflation rose 9.1% year-over-year, up from 8.6% the prior month. Core CPI fell to 5.9% from 6.0%. The core PCE has fallen from 5.3% in February to 4.7% in May. The Federal Reserve uses the core PCE rate to guide monetary policy. It will be interesting to see if they continue to do so over the next 12 months. People pay attention to the CPI since that’s what drives their spending. The Federal Reserve is a political animal despite its claims of independence. It is possible that it will tighten more aggressively as it feels pressure from politicians. Mid-term elections are nearing.
Interest Rates, Fed Policy, and the Economy
We have inflation because of poor Federal Reserve monetary policy and too much fiscal spending. Supply was constrained because of Covid. Demand increased due to low-interest rates and fiscal stimulus. Prices rise when supply falls and demand rises. The Federal Reserve is trying to contain inflation now by reducing demand. It is attempting to reduce demand by increasing the cost of money. (Interest is the cost of money.)
Likewise, fiscal spending is falling sharply in 2022. The Federal budget deficit was $2.8 trillion in 2021. The Congressional Budget Office (CBO) is forecasting a $1 trillion budget deficit for 2022. The drop of $1.8 trillion in spending represents 7.7% of Gross Domestic Product. Government spending is part of the GDP equation. GDP = C + G + I + Net Exports. The consumer is C, the government G, and business investment I.
Dr. Lacy Hunt from Hoisington has labeled the current situation a “Cost of Living Crisis”. Real income for full-time hourly and salaried workers has dropped by the fastest pace since 1980, he points out in Hoisington’s Q2 newsletter. He’s not surprised that the University of Michigan Consumer Sentiment survey is at its lowest level since it was created in 1952. Consumer confidence impacts consumer spending.
Hunt blames the Federal Reserve for the “Cost of Living Crisis” because he blames Fed policy for the currently high inflation rate. The data supports him. The Fed “has often boomed booms and slumped slumps” in Hunt’s words. What he means is that the Fed’s large swings in monetary policy have exacerbated existing trends. Too much easy money has caused higher inflation, as in the 1970s and today. Too many rate hikes have made recessions worse like in 1981-82, 2000-2002, and 2007-2009.
Money lubricates the economy. M2 is the best measure of money supply in that it tracks nominal GDP growth most closely. Other Deposit Liabilities (ODL) make up 80% of M2. ODL has risen at only a 0.4% annual rate the last 26 weeks, according to Hunt. ODL was rising at a 19.6% rate in 2020/21. It is the largest deceleration in deposit growth in nominal and real terms since the Great Depression, according to Hunt.
The odds of a soft landing are almost nil. The odds of a recession are close to 100%. The question is whether it has already begun. The follow-on question is how bad will it be? Norwood Economics is expecting a mild recession this year. The recession will be followed by a few quarters of growth as the Fed reverses course by Q4 and turns dovish. A mild recession in 2022 followed by a quarter or two of growth, and then we will see. A double-dip recession in 2023 is possible. The impact of quantitative tightening (QT) is a wild card. The Fed doesn't have much experience with QT. It is entirely possible that QT will put us right back in recession by the middle of 2023.
Regardless, the stock market is likely to trade sideways over the next 12-18 months. It remains a stock picker's market.
Regards,
Christopher R Norwood, CFA
Chief Market Strategist