Executive Summary
- December rate cut odds dropped to 60.2%
- Odds of rising inflation in 2025 are increasing
- Stock market is expensive at 21.4x earnings
- Diversification means owning something other than the S&P 500
- International markets are trading cheaply
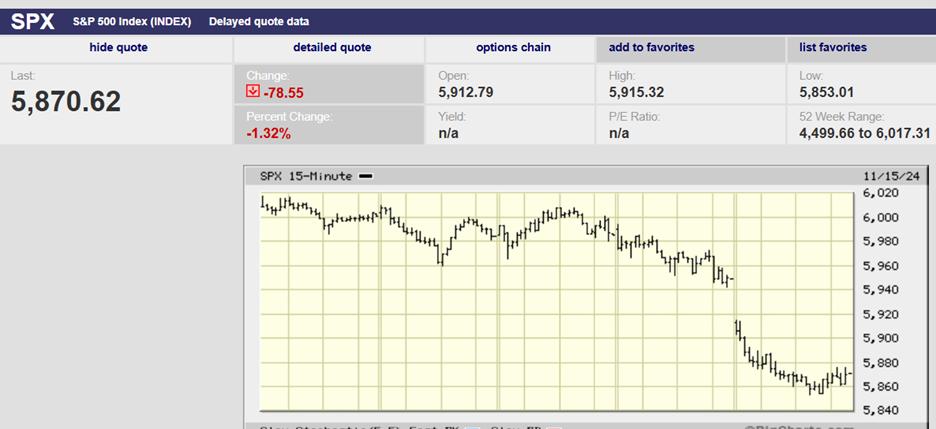
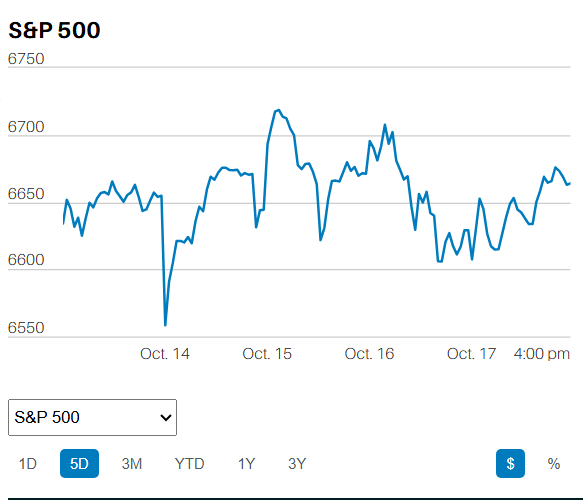
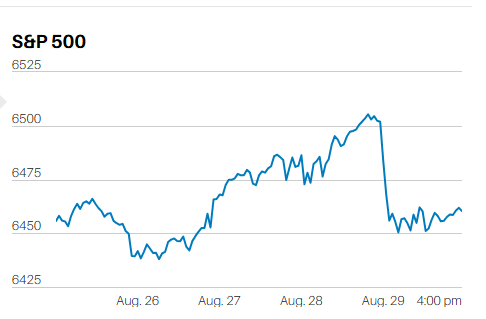
S&P 500 5-Day Chart
Market Update/Economic Update
The S&P 500 lost 2.1% last week. The index finished the week at 5870.62. Last week was the S&P’s worst since September 6th. Barron’s points to traders “once again focused on interest rates.” Odds of a December rate cut dropped to 60.2% according to the CME FedWatch tool. Norwood Economics wrote last week, “It believes continued rate cuts are a mistake. Financial conditions are already loose. The Trump administration plans to pass additional fiscal stimulus in the form of tax cuts. The odds of rising inflation in 2025 are increasing. To make matters worse, more tariffs will add to the inflationary pressures.” On a month-to-month basis, core CPI rose by 0.28% (3.4% annualized) in October from September. The Core PPI for final demand rose by 0.3% last month. Neither report supports more Fed rate cuts.
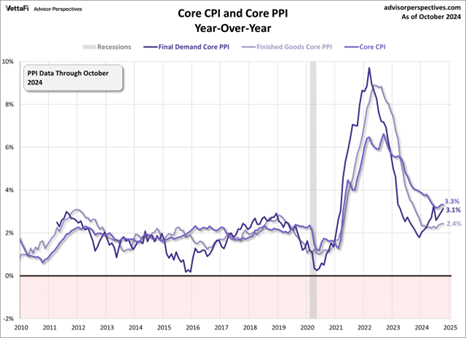
The Inflation rate is no longer falling.
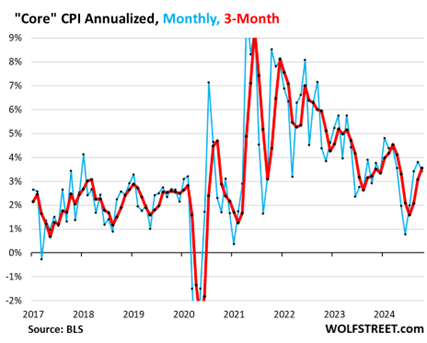
The three-month core CPI is rising.
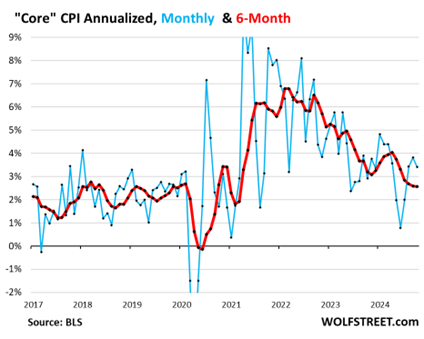
Six-month Core CPI is not rising yet but it’s falling at a decreasing rate.
Meanwhile, the Fed's preferred super core inflation measure rose by 0.31% in October. The super core measure excludes shelter from core services. Wage costs drive the super core measure. The annual rate of increase is 4.4% in October. A super core measure of 4.4% isn't conducive to a 2% inflation rate.
The inflation rate could average between 3% and 5% over the next one to two decades unless changes are made. Monetary policy needs to keep interest rates higher. Fiscal policy needs to reduce deficit spending. The $35 trillion public debt and 6.5% budget deficits make higher inflation likely. The Fed's easy money policy makes higher inflation likely as well. The 10-year Treasury yield will average at least 1% to 2% above the inflation rate if history is a guide. The age of zero real rates is behind us.
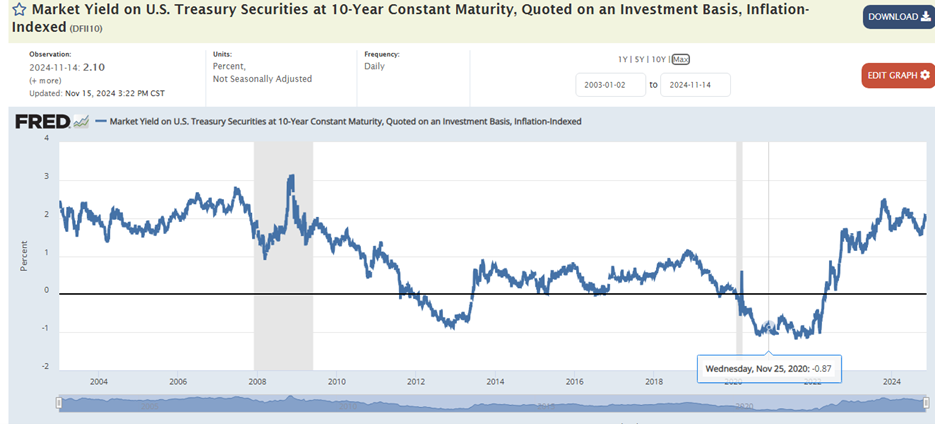
Inflation of 3% to 5% and a 10-year Treasury yield of 4% to 6% means bonds will remain attractive relative to stocks. That is unless the stock earnings yield rises. The S&P 500 has a 12-month forward price-to-earnings ratio currently of 21.4x. The earnings yield is the inverse of price-to-earnings. A P/E ratio of 21.4 equals an earnings yield of 4.7%. The 10-year Treasury yield ended the week at 4.44%. The equity risk premium is currently 0.26%, basically zero. An equity risk premium of 3% to 4% is normal, so an earnings yield of 7.7% to 8.7% would be an appropriate equity risk premium. An earnings yield of 7.7% equals a P/E ratio of 13x.
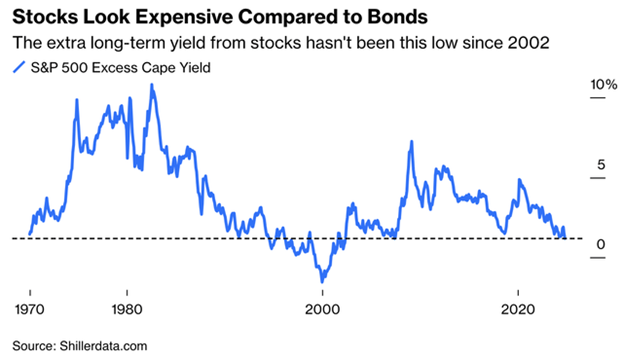
The stock market is expensive at 21.4x earnings (4.7% earnings yield) when the 10-year Treasury yields 4.44%. There is no margin of safety. The S&P will need to fall to somewhere around 3,700 for the equity risk premium to rise to 3% (4.44% plus 3% equals 7.44%. $274.6 in 2025 earnings divided by 7.44% equals 3,690. And that assumes the 12.7% earnings growth consensus forecast comes to pass. Earnings in 2025 are likely to rise in the single digits, not double digits.
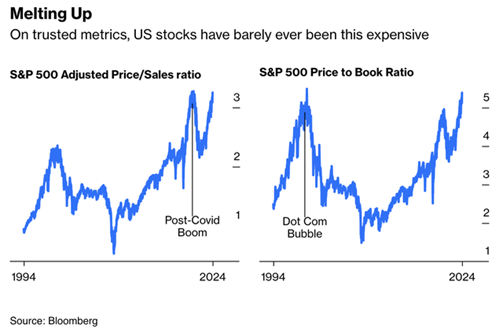
One last observation on stocks and inflation. Stock price-to-earnings multiples contract when inflation rates rise. Stock multiples contract because future earnings are worth less. Future earnings are worth less because inflation reduces the value of future dollars. The price-to-earnings ratio has fallen into the low double digits in the past when inflation rates rise. A multiple of 12x gives us an S&P value of around 3,300. Norwood Economics does not expect the S&P 500 to fall to 3,300 but it is a possibility.
Fortunately, other asset classes are cheaper than the S&P 500. Diversification means owning something other than the S&P 500. International developed and emerging market stocks are cheap. Also, the real 10-year Treasury yield is 1.96%, the highest real yield since before the Great Recession.
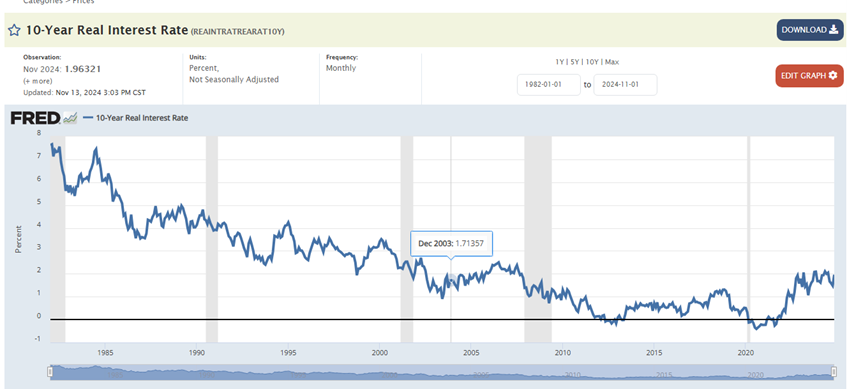
U.S. stocks are expensive because they have outrun earnings since the Great Recession.

U.S. stocks have had a great 10- and 15-year run
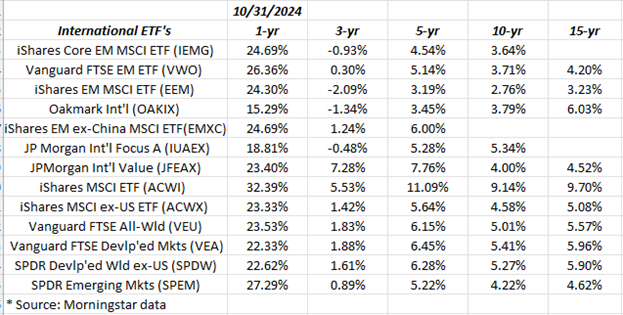
International markets have not done well over the last 10- and 15 years, making them cheap today.
The U.S. market has outperformed international markets by a wide margin. The U.S. market is trading at nosebleed levels. Meanwhile, international markets are trading cheaply. Fifteen years of going nowhere while earnings continue to grow make for an attractive opportunity. International stocks have underperformed U.S. stocks by a historic margin over the last 15 years.
Large-cap growth and tech market topped in March 2000. Money rotated into asset classes that had underperformed in the late 1990s. Value investing, small and mid-caps, and international equities began to outperform. The rally in international stocks lasted for 7 years. Meanwhile the S&P 500 and the Nasdaq fell 50% and 80% respectively between March 2000 and early 2003. History doesn’t repeat, said Mark Twain, but it does rhyme.
Regards,
Christopher R Norwood, CFA
Chief Market Strategist